An anatomic study that appeared recently in the American Journal of Sports Medicine1 identified - for the first time - the cross-sectional anatomy of the iliopsoas tendon at the level of the labrum.
The hip labrum is important because it maintains joint congruity, acts as a sealant to the hip joint, and maintains negative intra-articular pressure that stabilizes the hip joint.1-2 Surgeons have noted tight psoas tendons overlying and impinging on torn or inflamed anterior labrums.3 Ninety-two percent of labral lesions are in the anterior quadrant of the acetabulum and are related to degenerated hips.1
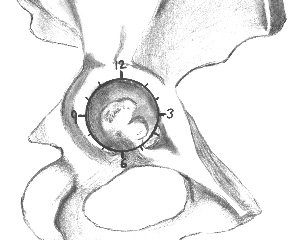 Labral tears at the 2 o’clock to 3 o’clock position of the acetabulum are directly under the iliopsoas tendon.
The above information is important since tightness of the iliopsoas should become a routine evaluation not only for hip patient complaints, but also as a preventative measure against hip pain and possible eventual degeneration. In a previous article,4 I discussed how a tight psoas can also be responsible for compressing the hip capsule. Tightness of the hip capsule can create an increase in the intra-articular pressure. High pressure within the hip capsule creates high intraosseous venous pressure due to blockage of flow in the periarticular veins, such that hemodynamic changes in the bone marrow are secondary to high pressure within the capsule.5
Labral tears at the 2 o’clock to 3 o’clock position of the acetabulum are directly under the iliopsoas tendon.
The above information is important since tightness of the iliopsoas should become a routine evaluation not only for hip patient complaints, but also as a preventative measure against hip pain and possible eventual degeneration. In a previous article,4 I discussed how a tight psoas can also be responsible for compressing the hip capsule. Tightness of the hip capsule can create an increase in the intra-articular pressure. High pressure within the hip capsule creates high intraosseous venous pressure due to blockage of flow in the periarticular veins, such that hemodynamic changes in the bone marrow are secondary to high pressure within the capsule.5
The iliopsoas can be stretched by methods such as post-facilitation stretching, fascial release, and active isolated stretching6 (also discussed previously); friction massage or Graston Technique at the insertion on the lesser trochanter can also be beneficial. Treating the psoas also requires evaluation and treatment of hip mobility. Loss of hip motion can be directly related to restricted myofascia, and restricted fascia could be due to loss of joint motion. Both must be considered. Reflex inhibition of tight myofascia can be responsible for a tight hip capsule, rather than capsular contraction.
Ferguson7 states that to create absolute lengthening of the psoas, it is necessary to normalize femoral/acetabular dysfunction (F/A), just as normal F/A function will depend on a fully lengthened psoas. Hip joint-play dysfunction should be evaluated. There will never be normal joint function if myofascial dysfunction abnormally stresses the joint, nor can there be normal myofascial function if there is joint dysfunction. Normal muscle length requires normal joint function.4
Patients with labral tears usually complain of groin pain, a clicking hip, sharp, catching pain and popping. Sometimes the pain may be localized to the anterior groin, just proximal to the trochanter, or deep within the buttock.7 The hip symptoms may be subtle, such as a dull activity-related or positional pain that just does not seem to improve. I have treated patients with these types of symptoms and some of them definitely had shortened iliopsoas muscles. One was diagnosed with iliopsoas tendinosis and labral tearing that responded to manual therapy over the insertional tendinosis area.
References
- Alpert JM, Kozanek M, Guoan Li, Kelly BT. Cross-sectional analysis of the iliopsoas tendon and its relationship to the acetabular labrum: an anatomic study. Am J Sports Med, 2009;37(8):1594-1598.
- Dobbs MB, Gordon JE, Luhmann SJ, Szymanski DA, et al. Surgical correction of the snapping iliopsoas tendon in adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg (U.S.), 2002;84:420-424.
- Heyworht BE, Shindle MK, Voos JE, et al. Radiologic and intraoperative findings in revision hip arthroscopy. Arthroscopy, 2007;23:1295-1302.
- Hammer W. “The Iliopsoas and the Hip Vascular-Compression Theory.” Dynamic Chiropractic, March 26, 2007.
- Goodard JN, Gosling PT. Intra-articular fluid pressure and pain in osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg (U.K.), 1988:52-55.
- Hammer W. “The Psoas Major May Not Function As You Think.” Dynamic Chiropractic, Jan. 29, 2008.
- Mason JB. Acetabular labral tears in the athlete. Clin Sports Med, 2001;20:779-790.
Click here for previous articles by Warren Hammer, MS, DC, DABCO.