Taking a page from Stacy and Clinton of The Learning Channel's hit television program, "What Not to Wear," we recently published an article in the summer issue of Chiropractic History: The Archives and Journal of the Association for the History of Chiropractic, that explores the evolution of physician attire from prehistoric times to the present.1 We also focused on the most recent articles from the indexed literature related to patient preferences for their doctors' clothing.
Historical Perspective
Primitive peoples looked to witch doctors and medicine men to banish what they perceived to be the causes of illness: demons, evil sorcery or the malevolent influences of spirits. To expel these forces, healers performed ritual dances and incantations while dressed in animal skins and other flamboyant attire to inspire confidence in their supernatural powers.
As man advanced, the influence of Hippocrates and his disciples prevailed. In the Hippocratic sphere of influence, a physician dressed well in clothes contemporary to the times.
In the Middle Ages, medical treatments fell out of favor, as they were based upon the false premise of balancing the four humours of blood, black bile, yellow bile and phlegm. Believing disease was a punishment for transgressions against God or their fellow man, priests and clerics assumed the role of healers, dressed in the robes of the church.
Later, when the bubonic plague visited Europe, a new healer came to the forefront: the plague doctor. The plague doctor donned a protective uniform including a black waxed robe, beaked mask and wide-brimmed hat. Up until the late 19th century, physicians wore black – considered a more formal color of dress – to reflect the seriousness of patient-doctor interactions.
In the early 20th century, not long after Lister's introduction of antiseptic conditions and Flexner's scathing report on the state of medical education, physicians adopted the respected garb of laboratory science, the white coat, as a means of distancing allopathy from the quackery and superstition of 19th century medicine.
Today, less formal attire has invaded modern business and health care. We were curious as to patient preferences regarding this shift, and conducted a review of the indexed literature to see what, if any, data exist and implications for current practice.
Findings From Recent Surveys
No studies were located pertaining to patient preferences for attire specifically related to chiropractic physicians; however, 13 survey studies were identified in the indexed literature between 1998 and 2014 regarding physicians in general. These studies, conducted in Israel, the United States, Canada, England and Japan, represent 4,327 respondents ranging in age from 14 to 90 years. [See Table below]
These investigations utilized questionnaires with varying methodologies in an array of settings including surgeon and hospital outpatient clinics, emergency departments, primary care settings and pharmacies. Some researchers included photographs of physicians in differing attire ranging from traditional business clothing, with or without the white lab coat, to jeans and/or short skirts for women, T-shirts and athletic shoes. Other studies reported patient opinion using written surveys.
In general, more formal attire (dress clothing including ties, dress pants and dress shirts, skirts or dresses for women, closed-toe dress shoes) versus casual clothing (e.g., golf shirts, casual / athletic shoes, jeans) was preferred in most instances. The white lab coat was the predominant affirmative finding among these surveys.
Conversely, two investigations found no difference in patient preferences regarding surgical scrubs and traditional business attire with the white coat. One study from an urban emergency department suggested three possible reasons for this conflicting finding: 1) Emergency room visits are unplanned and patients may expect less formality; 2) Patients are often in distress in the emergency department and may pay less attention to physician attire; and 3) Media may bias patients' expectations, as many television programs depict emergency-room physicians in surgical scrubs.
Some of the surveys reported extremely specific negative findings. For men, long hair / ponytails, earrings and open collars or collarless shirts were not preferred or carried negative associations for patients. For women, mini-dresses, shorts, tight-fitting clothes and perfume provoked negative responses. For both genders, blue jeans, surgical scrubs, and athletic shoes, sandals, or clogs were considered negative attributes.
Perhaps most interesting are the findings in regards to physician attire relative to 1) patient confidence in the physician's ability; 2) commitment to adhere to prescribed therapy; 3) desire to return for follow-up care; and 4) patient confidence in their physician. A more formally dressed physician positively impacted those four attributes.
The "branding" of the physician in the white laboratory coat has been exceptionally successful. In spite of a cultural move toward more casual attire in business, the studies in our review contend the majority of patients still wish to see their physician dressed in the traditional garb established more than 100 years ago.
We were disappointed to find no studies in the indexed literature regarding patient preferences for chiropractic physicians. As a result, we contacted Dynamic Chiropractic with a request to conduct an informal Internet poll of the clothing chiropractic physicians wear in their own practices.
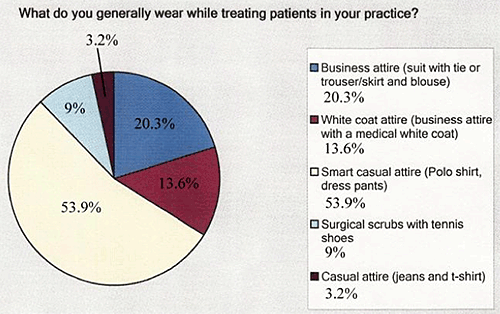
Results of this poll of 345 chiropractic physicians revealed that almost 54 percent of DCs polled wear what was termed smart casual dress, which includes polo-type collared casual shirts with dress pants. Only 13.6 percent in this sample wear more traditional business attire with the white coat. Whether or not this more casual approach endears chiropractors to patients or repels them awaits further investigation.
Figure 1. Internet survey of DCs
Summing Up
Physician attire has been an important part of the healing experience from prehistoric times to the present. Despite the move away from traditional formal attire in American business culture, recent evidence suggests patients still prefer to see their allopathic physician in dress shirt and pants, tie, dress shoes; skirts or dresses for women physicians; and white laboratory coats.
Medicine has been successful in branding itself as a modern, scientific practice in part by cloaking itself in the most recognized symbol of laboratory science – the white coat. Chiropractic does not enjoy the cultural authority of medicine, perhaps because we have failed to brand ourselves in a likewise fashion. We do not know if the findings summarized here translate to patient preferences for chiropractic patients. However, our strong suspicion is that they do, because we practice alongside our allopathic counterparts in the health care arena in competition for many of the same patients.
Table 1. Findings of recent studies in the English indexed literature regarding physician attire.
| Citation | Practice Type/Setting | Methodology | # of Subjects & Demographics | Positive Findings | Negative Findings |
| Menahen, S. and Shvartzman P. (1998) Is our appearance important to our patients? Family Practice, 15(5), 391-97 | Family Practice / Isreal | Photographs of the same physician (both male and female) in differing clothing from traditional to casual | 168 patients aged 14 years of age and older. | Male Physician: white coat, dress shirt/suit and tie, name badge. Female Physician: white coat, dress shirt and trousers, name badge. |
Male Physician: Long hair, earrings. Female Physician: mini-dress, shorts, tight-fitting clothes. |
| Kanzler, H. and Gorsulowsky D.C. (2002) Patients' attitudes regarding physical characteristics of medical care providers in dermatologic practices. Arch Dermatol, 138, 463-66 | Outpatient dermatologic clinical practices (one in a county hospital, one private practice). | Written survey offered to all patients seen in a 1-week period. | 275 patients (84 from private practice / 191 from the county hospital), 24 years of age and older. | Male Physician: white coat, dress shoes, dress pants, ties, name badge. Female Physician: white coat, dress shoes, skirts/dresses or dress pants, name badge. |
Blue jeans, clogs, sandals, surgical scrubs, cologne. Specifically for males: long hair / pony tails and earrings. |
| Cha, A., Hecht B.R., Nelson K., Hopkins, M. Resident physician attire: does it make a difference to our patients? Am J Obstetrics and Gynecology, 190, 1484-88 | Ohio hospital-based OBGYN clinic | Questionnaire posed to patients based on photographs of resident physicians in varying attire, rating responses on a 5-point Likert scale. | 184 patients, 18 years of age and older, receiving care from resident physicians. | "...more formal physician attire (particularly the white coat) was preferred over casual clothes." | "Figure 3 depicts the responses to the questions ... This figure shows that as the clothing style moves from the more clinical / formal attire to the more casual, the comfort of the patient in talking with their physician declines, and the confidence the patient has in the ability of the physician also declines." |
| Keenum, A.J., Silver-Wallace, L., Barger-Stevens, A.R. (2003). Patient's attitudes regarding physical characteristics of family practice physicians. Southern Medical Journal, 96(12), 1190-94. | Family practice clinics in Knoxville, TN | Descriptive cross-sectional survey regarding characteristics of physician appearance. | 496 patients; 73% women, 27% mean; 57% were 40 years of age or below. | Name tag, white coat, visible stethoscope. | Male Physician: earrings, ponytails / long hair, and open shirts. Female Physician: perfume. All should avoid sandals, clogs, tennis shoes. |
| Rowland, P.A., Coe, N.P.W., Burchard, K.W., Pricolo, V.E. (2005). Factors affecting the professional image of physicians. Current Surgery, 62(2), 214-19. | Convenience sample of raters selected from populations of undergraduate college students, subjects over 60 years of age and 70 surgeons from the U.S. and Canada. | Ten slides of actual practicing physicians in varying attire were rated for preference. The depicted physicians represented males and females ranging from 26-58 years of age with varying ethnic and religious affiliations. Each physician was rated on a Likert scale for 10 different attributes. | 234 undergraduate students, 19-22 years of age; 59 elderly subjects, 60+ years of age; 70 surgeons from the U.S. and Canada, 30-50 years of age. | Male Physician: white dress shirt, dress pants, white lab coat, tied leather shoes and belt, traditional tie, conservative hairstyle and limited jewelry. Female Physician: solid color skirts, hair length above the shoulder, white lab coat, limited jewelry, closed-toe shoes and collared blouse. |
Too many colors in clothing choice, casual shoes, a stethoscope around the neck, unkempt hair and casual slacks. |
| Major, K., Hayase, Y., Balderrama, D., Lefor, A.T. (2005). Attitudes regarding surgeons' attire. Excerpta Medica, 190, 103-6. | Urban teaching hospital and internet survey. | Questionnaire of 8 statements regarding surgeon attire and professional demeanor – responses of agree, disagree, or no opinion. | 38 surgeons, 38 consecutive surgical inpatients, and 343 non-hospitalized public subjects. | "Uniform of a doctor" including white coat and nametag. Patients preferred to be called by their surname. | Patients were offended when their surgeon wore scrubs, clogs, blue jeans, and tennis shoes. |
| Rehman, S.U., Nietert, P.J., Cope, D.W., Kilpatrick, A.O. (2005). What to wear today? Effect of doctors' attire on the trust and confidence of patients. Am J of Medicine, 118, 1279-86. | Internal medicine outpatient clinic in a VA medical center. | Cross-sectional survey after reviewing pictures of physicians in four different dress styles. Questions were posed regarding preference for physician attire, trust and willingness to discuss sensitive issues based on impressions of various physician pictures. | 400 respondents; 54% men, 46% women, mean age of 52.4 years, 58% Caucasian, 38% African-American, 43% had greater than a high-school diploma. | Overwhelmingly patients preferred a physician in professional attire: white coat, dress shirt, dress pants, leather shoes, tie for men, collared blouse for women. Trust and willingness to discuss sensitive health issues with physicians dressed in professional attire was also favored. Professional attire was associated with "respondent commitment to adhere to prescribed therapy and an expressed desire to return for follow-up visits." | Casual attire (blue jeans, tennis shoes, collarless shirt) consistently scored lowest for all perceived physician attributes. |
| Li, S.F., Haber, M. (2004). Patient attitudes toward emergency physician attire. J Emerg Med, 29(1), 1-3. | Urban emergency department in a teaching hospital. | Convenience sample survey of patients presenting over a 2-week period. In week 1, ED physicians wore professional attire (white coat, dress shirt and pants). In week 2, ED physicians wore surgical scrubs. | 111 patients surveyed; 56 in formal attire group and 55 in surgical scrub group. Age range 18-75 years of age, with a mean of 42 years of age. 65% female, 35% male, 65% Hispanic, 29% African-American, 5% Caucasian. | "Patient evaluations of satisfaction, physician appearance, and physician professionalism were not affected by physician attire. In fact, the scores between the two types of dress styles were nearly identical." | Reasons for less importance in the ED: 1. Visits are unplanned and patients may expect less formality. 2. Patients are often in distress in the ED and may pay less attention to physician attire. 3. Media may bias patient expectations as many TV programs depict ED physicians in surgical scrubs. |
| Gherardi, G., Cameron, J., West, A., Crossley, M. (2009). Are we dressed to impress? A descriptive survey of assessing patients' preference of doctors' attire in the hospital setting. Clinical Med, 9(6), 519-24. | Three academic primary care offices in South Carolina and Ohio in 2010. | Survey of patients preferences regarding physician attire and how each patient's individual doctor dressed. A statement was provided about the possible contamination of coats and ties worn by physicians and preferences were then reassessed. | 423 surveys were returned, 67% female, 25% male, 8% failed to specify. 24% 18-30 years of age; 20% 31-45 years of age; 28% 46-60 years of age; 23% over 60 years of age; 5% did not specify age. | 44% of respondents preferred physician in a white coat and combined data suggest 57% preferred more formal attire (dress shirt and pants with tie for males or dress if female) versus more casual dress or surgical scrubs. | Surgical scrubs were the only attire that appeared to be viewed unfavorably. After viewing the statement about clothing contamination, 45% who initially favored a white coat and/or tie, remained in favor of a white coat and/or tie while 41% initially in favor of the white coat and/or tie stated their opinion had changed. |
| Edwards, R.D., Saladyga, A.T., Schriver, J.P. Davis, K.G. (2012). Patient attitudes to surgeons' attire in an outpatient clinic setting: substance over style. Am J of Surg. 204, 663-65. | Surgeon outpatient clinics. | Prospective survey study of patient preferences. In a first 12-week period, physicians wore white coats and surgical scrubs, in the second 12-week period, physicians wore traditional clothing and surgical scrubs were prohibited in the outpatient clinic. | 570 patient surveys, 51% seen by physicians in surgical scrubs and white coats, 48% by physicians in traditional attire. | "Our study demonstrates that most of our patients do not feel that surgical scrubs are inappropriate clothing or that the surgeon's attire influenced their opinion of the care that they received." | ". . . patients seen by physicians wearing scrubs had a more negative attitude regarding tennis shoes and clogs . . ." |
| Oschsner J., Landry, M., Dornelles, A.C., Hayek, G., Deichmann, R.E., (2013). Patient preferences for doctor attire: The white coat's place in the medical profession. The Oschsner Journal. 13(3), 334-42. | Hospital-based internal medicine clinic, community-based outpatient family practice clinic, and an inpatient hospital ward in Jefferson, LA. | Cross-sectional, observational study survey. | 153 patient surveys, 67.6% female and 66.7% Caucasian. Mean age of patients was 55.5 years with a range of 19-90. | Patients overwhelmingly (~70%) preferred physicians in white coats; of those preferring a white coat also preferred it with traditional dress clothing (dress shirt and pants with a tie) versus a white coat with surgical scrubs. "Our results suggest that coats make a tangible contribution to a patient's sense of confidence and comfort with a physician." | "Respondents also noted that the individual appeared 'unclean', 'sloppy', and 'unprofessional' without the white coat attire." |
| Kurihara, H., Maeno, T., Maeno, T. (2014). Importance of physicians' attire: Factors influencing the impression it makes on patients, a cross-sectional study. Asia Pac Fam Med. 13(1), 2. (Published online) | Five pharmacies across Japan from April to October, 2012. | Survey of preferences by those completing the questionnaire. | 491 complete surveys, mean age 51.9 years, 40.3% male. | White coat with dress clothing (dress shirt/tie and dress pants for male, skirt and collared blouse for female) was judged to be the most appropriate attire for physicians by survey respondents. This attire was one of the most important factors inspiring confidence in physicians by patients. |
Reference
- Troyanovich S, Troyanovich J. Do the clothes make the healer: a history of physician attire from prehistoric times to the present with implications for current practice. Chiropractic History, 2015;35(1):47-57.
Dr. Steve Troyanovich is the secretary of the Association for the History of Chiropractic. Contact him with questions and comments at
. The AHC has preserved the credible history of the profession as its sole mission through the publication of the scholarly journal, Chiropractic History. Stories such as this one may be accessed through the pages of the AHC's journal (www.historyofchiropractic.org).
Jennifer D. Troyanovich is president of the Central Illinois Neuroscience Foundation in Bloomington, Ill.